News
Invasive Trees and Grasses in Australia: Causes, Impacts and Solutions
Invasive Trees and Grasses in Australia: Causes, Impacts and Solutions
Invasive species can outcompete and displace native plants, degrade the soil quality and fertility, increase the water loss and erosion, and increase the fire risk and greenhouse gas emissions.
The financial cost is already enormous. Invasive species – predominantly weeds, cats, rabbits, and fire ants – are conservatively estimated to have cost Australia $390 billion over the past 60 years (about $25 million per year) in impacts and control measures.
Treating prevalent invasive plants on your acreage
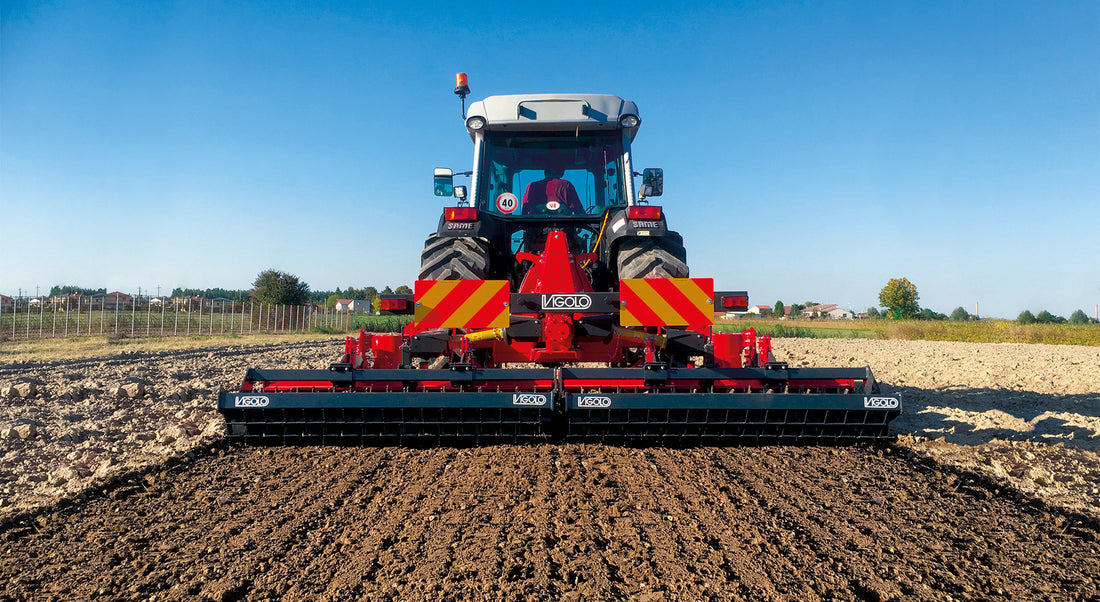
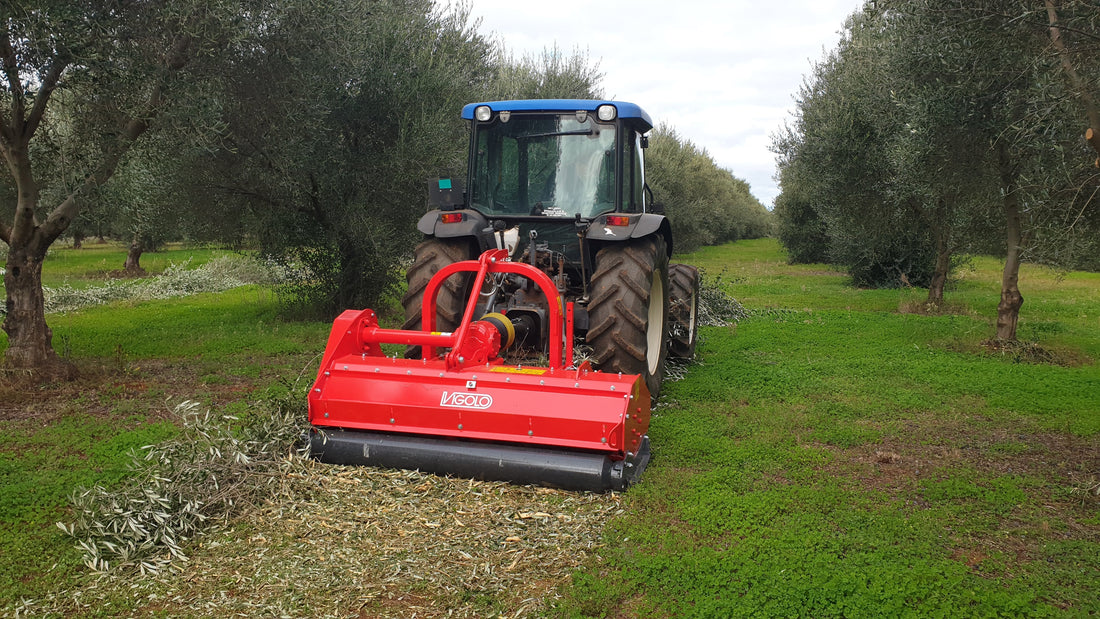
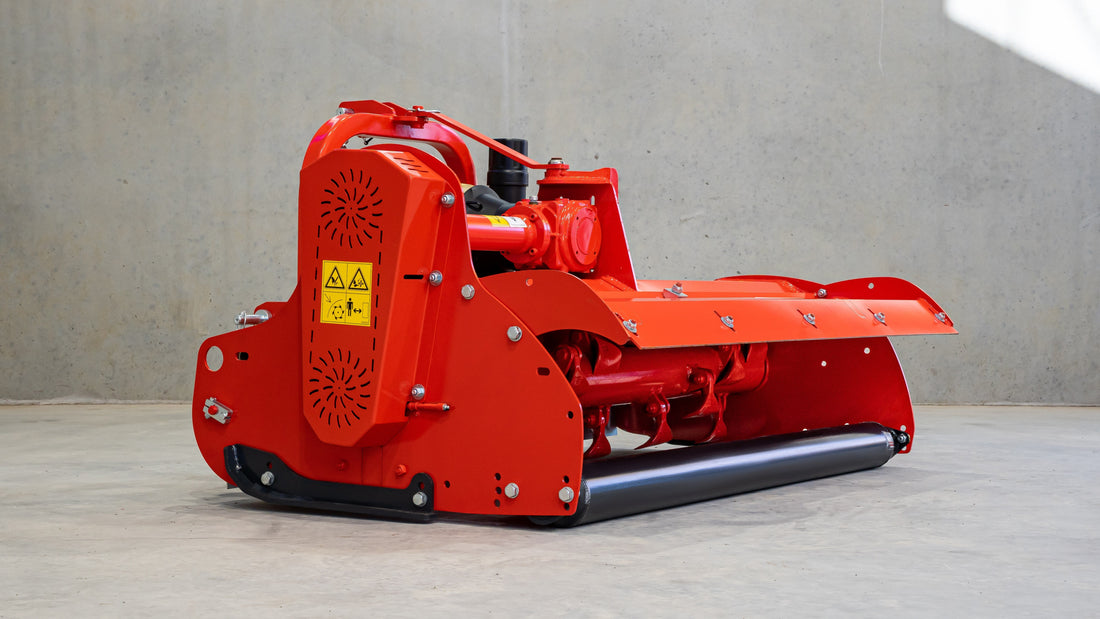
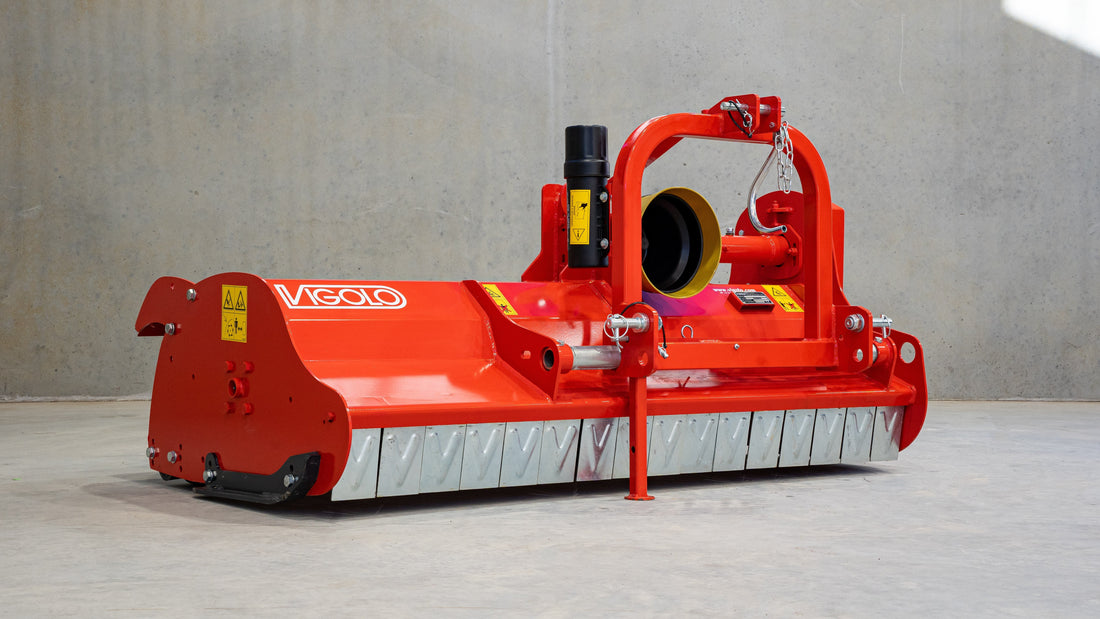
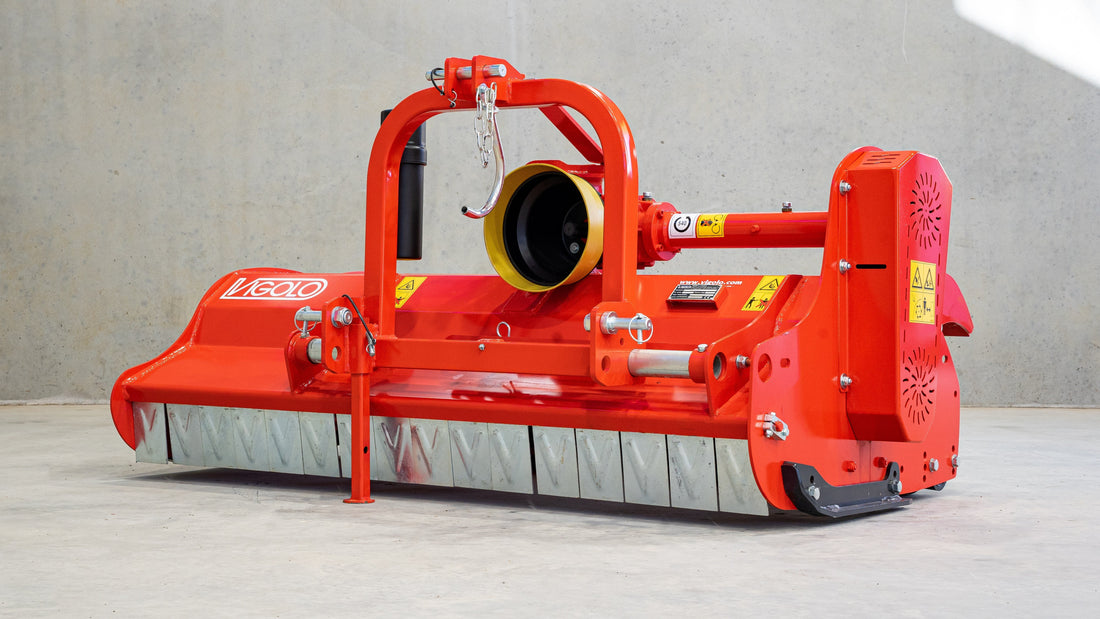
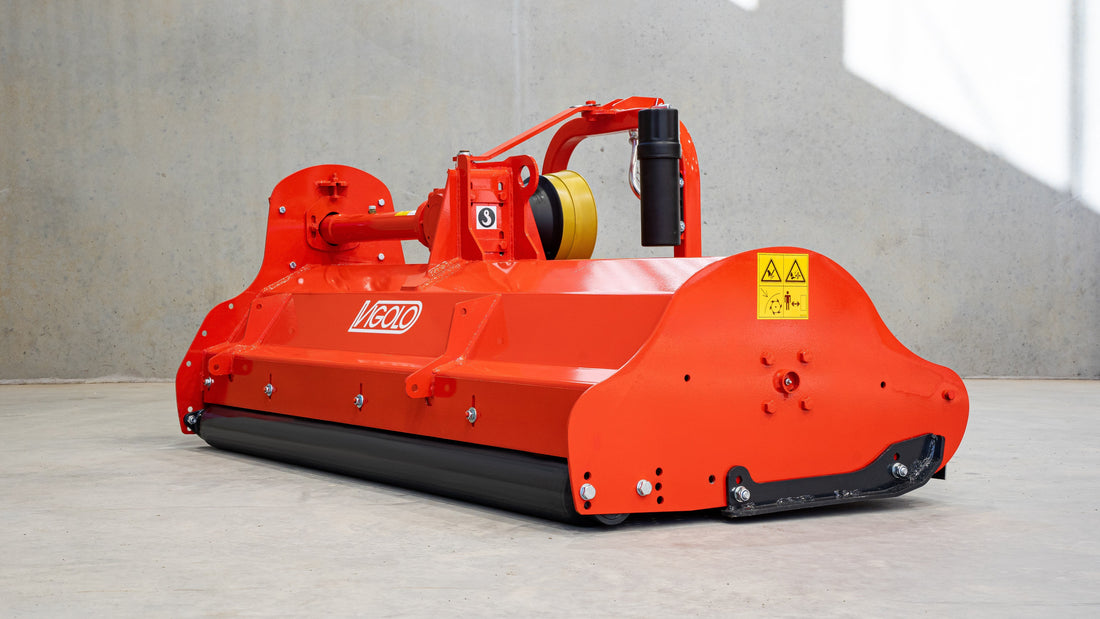
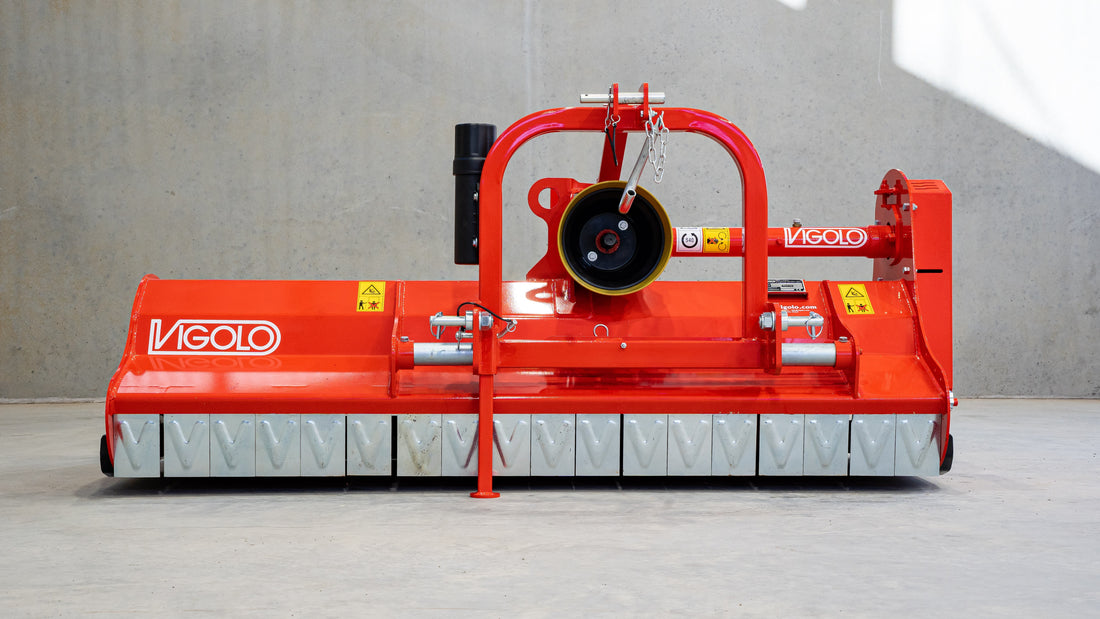
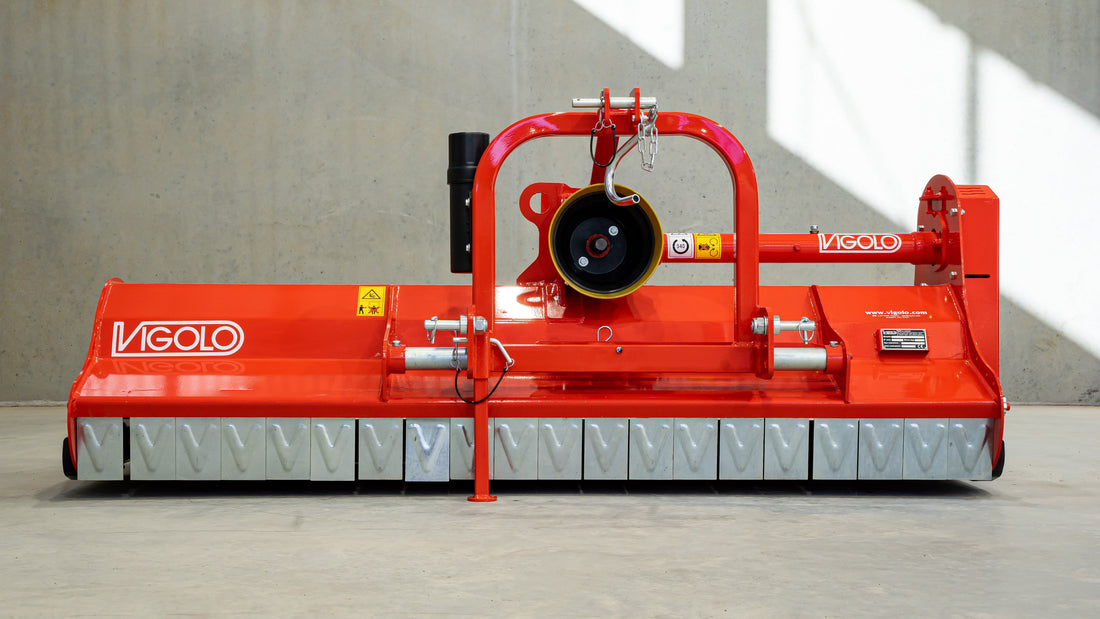
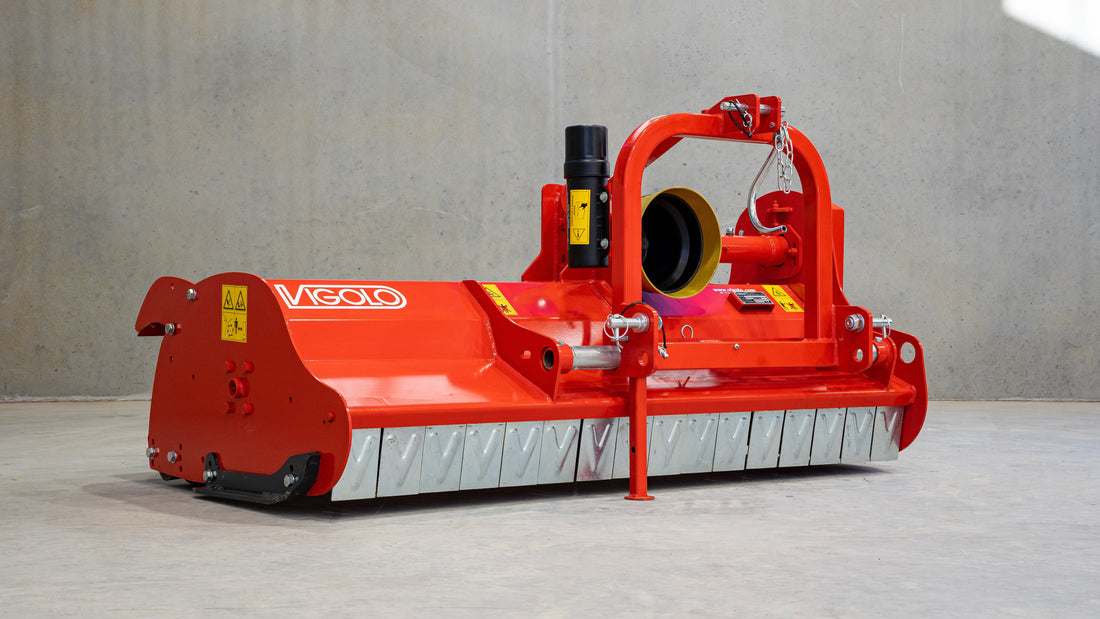
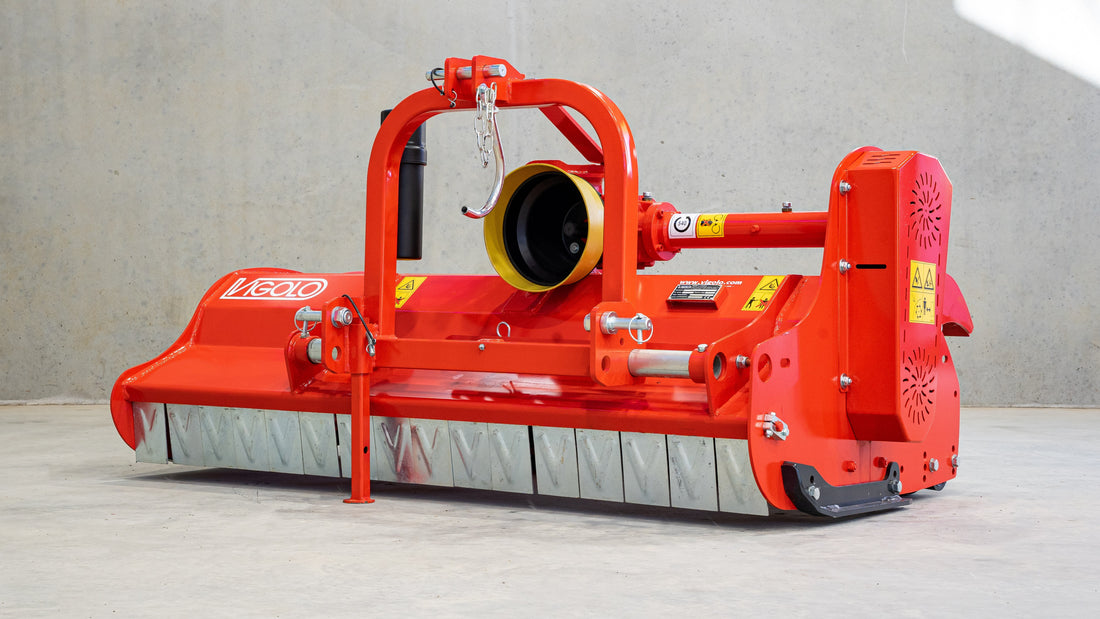
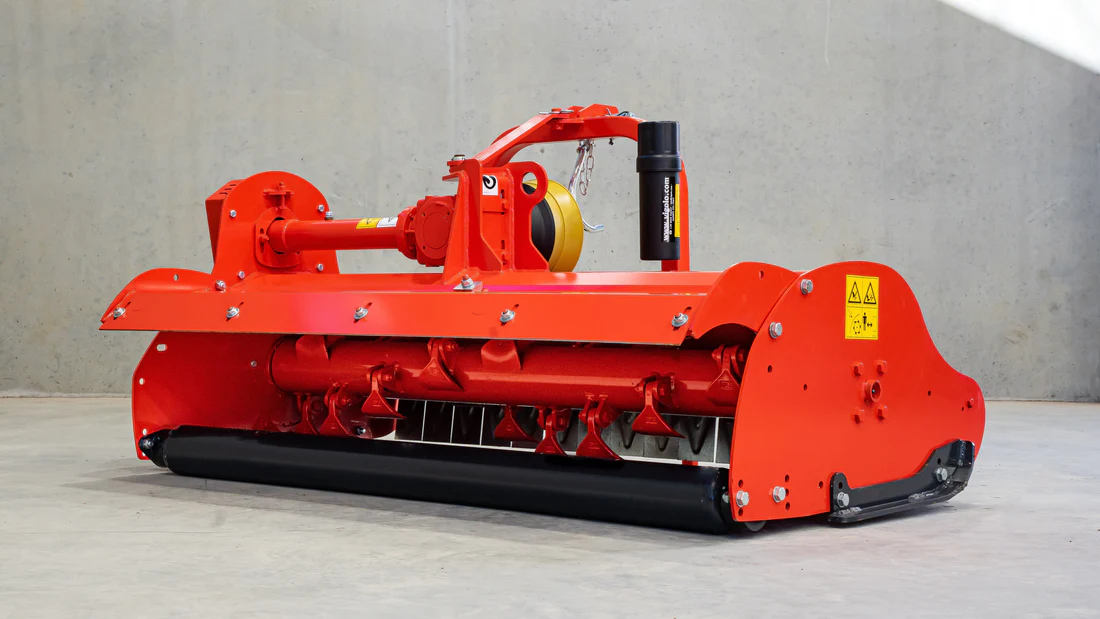
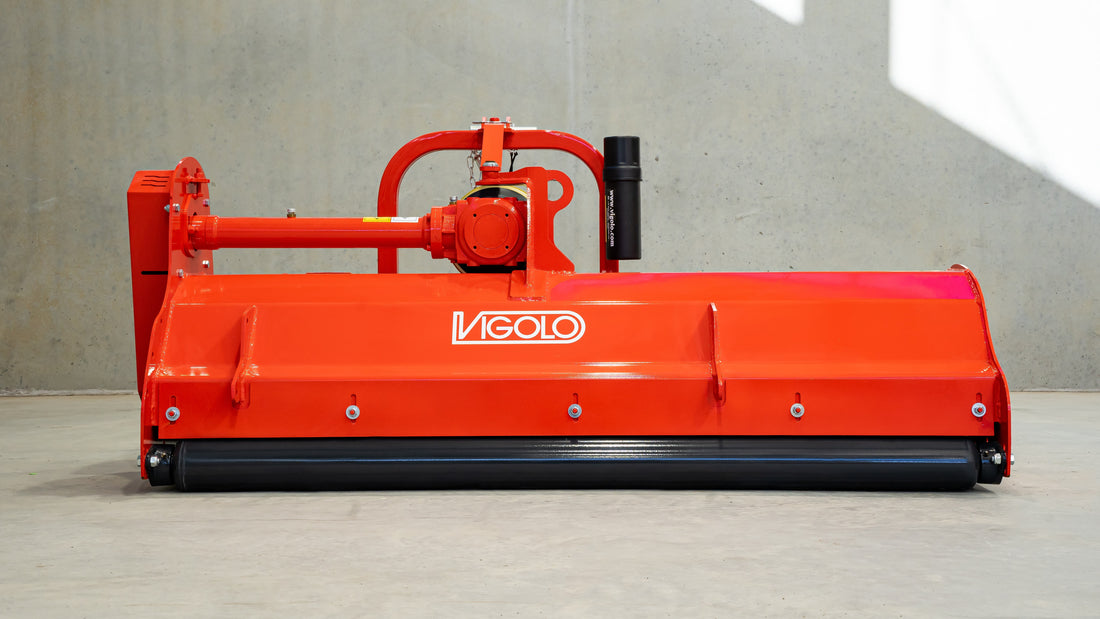
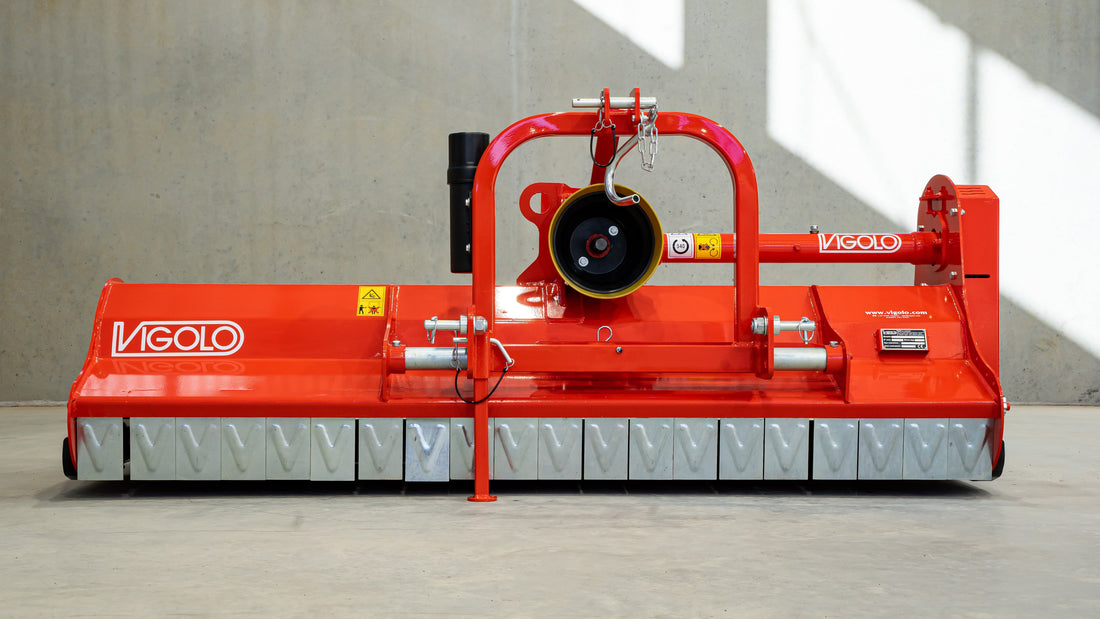
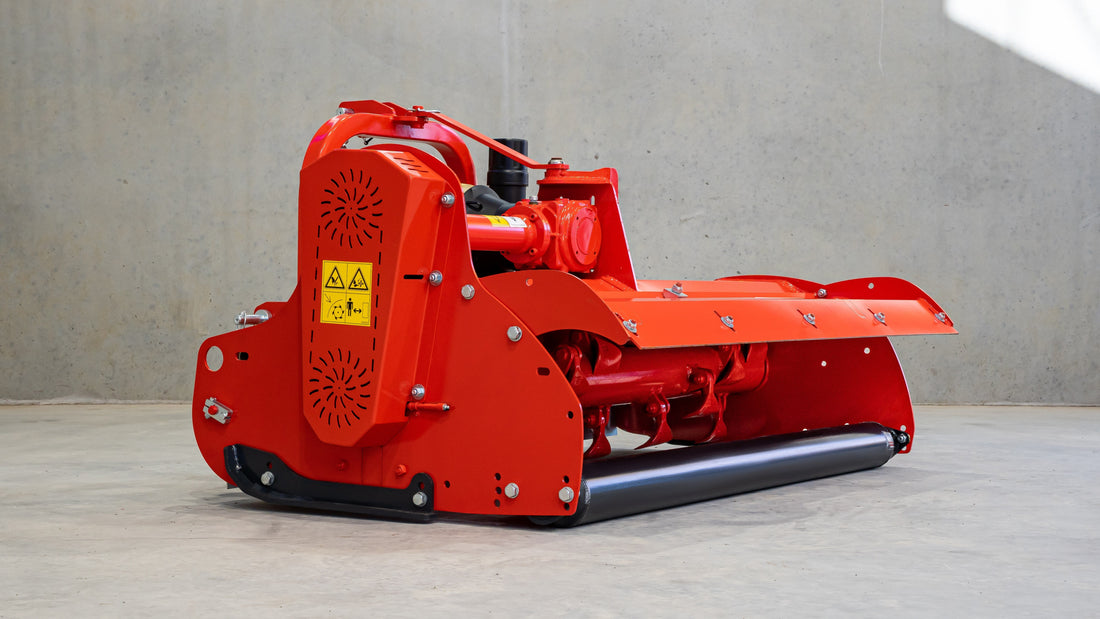
Mulcher treatment is a method of controlling invasive species by using a machine that cuts and shreds the plants into small pieces and distributes them over the ground. This can reduce the biomass and seed production of the invasive grasses and improve the soil quality and moisture retention.
Mulcher treatment can also suppress the regrowth of invasive grasses and create a favourable environment for the native plants and animals. Mulcher treatment can be used for most types of invasive trees and grasses, but some factors that may influence its effectiveness are the size and density of the invasive grasses, the type and condition of the soil, the type and height of the mulcher, and the type and speed of the blades.
Common invasive grasses on farmland and acreage
Whilst this is not a comprehensive list of invasive grass species in Australia, these are some of the common reported weeds treatable with regular mulching. Declared weed status of these species may vary from state to state.
- Tamarisk (salt cedar): This is a woody shrub or small tree that grows along watercourses and wetlands and can consume large amounts of water and increase soil salinity.
- Pinyon-juniper: This is a group of coniferous trees that can form dense woodlands and displace native grasses and shrubs and reduce the habitat for wildlife.
- Russian olive: This is a deciduous tree that can invade riparian areas and outcompete native plants for water and nutrients and alter the soil chemistry.
- Red cedar: This is an evergreen tree that can spread rapidly and form dense thickets and reduce the diversity and productivity of native vegetation.
- Buckthorn: This is a deciduous shrub or small tree that can invade woodlands, grasslands, and wetlands, and produce large amounts of seeds that are dispersed by birds and animals and inhibit the growth of other plants.
- Multiflora rose: This is a thorny shrub that can form impenetrable thickets and smother native plants and provide shelter for pest animals such as rabbits and foxes.
- Blackberry: This is a prickly shrub that can grow in a variety of habitats and produce large amounts of fruits that are eaten and spread by birds and animals and create dense mats that prevent the regeneration of native plants.
- Lantana: This is a woody shrub that can grow in disturbed areas and produce colourful flowers that attract pollinators and displace native plants and produce toxic berries that can poison livestock and wildlife.
Common invasive tree species on the Eastern Seaboard
Like invasive grasses, invasive and fast spreading tree species can also cause big problems for landowners, graziers, and anyone on acreage.

- African Olive (Olea europaea subsp. cuspidate): This is a tall shrub or small tree that can form dense thickets and outcompete native plants for water and nutrients. It is mainly found in NSW, but also occurs in SA, Vic., and Qld.
- Arabian Coffee (Coffea arabica): This is a shrub or small tree that can grow under very low light intensity and invade rainforest types. It is mainly found in Qld, but also occurs in NSW and NT.
- Camphor Laurel (Cinnamomum camphor): This is a large evergreen tree that can produce large amounts of seeds and spread rapidly. It can alter the soil chemistry and reduce the diversity of native plants and animals. It is mainly found in NSW and Qld, but also occurs in Vic., SA, and WA.
- Cocos Palm (Syagrus romanzoffiana): This is a tall palm tree that can produce large clusters of fruits that are eaten and dispersed by birds and bats. It can invade a variety of habitats and displace native vegetation. It is mainly found in Qld, but also occurs in NSW, NT and WA.
- Willow (Salix spp.): This is a group of deciduous trees that can grow along watercourses and wetlands and produce large amounts of roots and branches that can block water flow and increase erosion. It can also hybridise with native species and reduce their genetic diversity. It is mainly found in NSW, Vic., SA, and Tas., but also occurs in Qld, WA, and ACT.
This is not a comprehensive list of invasive tree species in Australia, and the declared weed status of these species may vary from state to state. Therefore, it is advisable to check with your local authorities before planting, removing, or controlling any of these species. Check relevant local databases of invasive plants and their management options.